See examples of how perfectly competitive firms decide how much to produce. Entry to the market is limited.
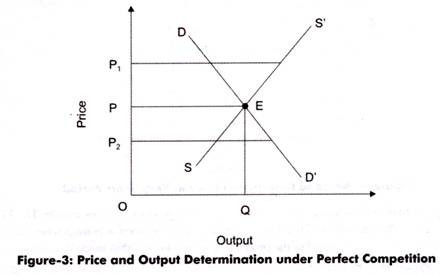
Price And Output Determination Under Perfect Competition
In perfect competition any profit-maximizing producer has a market price equal to its marginal cost PMC.
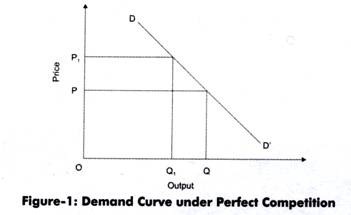
. Example of Optimal Price and Output in Perfectly Competitive Markets. Suppliers can only supply what the consumers can consume at given prices. Business managers are expected to make perfect decisions based on their knowledge and judgment.
MC AR e-1e Exhibit-2. The extra revenue gained from each extra unit sold is therefore the market price. E Price elasticity of demand.
Describe prices and output in a perfectly competitive market. Therefore the firm can alter the quantity of its output without changing the price of the product. In a perfectly competitive market a firm cannot change the price of a product by modifying the quantity of its output.
The total revenue for a firm in a perfectly competitive market is the product of price and quantity TR P Q. Group of answer choices Buyers and sellers are price takers. The price increases in the short run from 170 per bushel to 230.
The firm will attempt to run competitors out of business to increase profits. Further the input and cost conditions are given. The profit is maximized when.
Price determination is one of the most crucial aspects in economics. Competitive Supply where marginal cost equals price. Each firm sells a virtually identical product.
We know that a firm is in equilibrium when its profits are maximum which relies on the cost and revenue. Which of the following statements does not describe a perfectly competitive market. In competition output is pressed to the point where marginal cost equals the market price.
Since every economic activity in the market is measured as per. Output Marginal Cost AVC ATC cases per week per case per case PER CASE 150 600 880 1650 200 640 780 1360 250 700 700 1164 300 765 710 1097 350 840 720 1052 400 1040 750 1040. Prices are the lowest sustainable price possible.
Up to 10 cash back Example Question 1. In a perfectly competitive market structure the market sets the price and firms are merely price takers and therefore operate for as long as production costs fall below revenue. This is why the demand curve.
As in equilibrium MRMC. Under perfect competition there are many small firms each producing an identical product and each too small to affect the market price. Compared to a perfectly competitive market a monopolist produces.
Output is where the supplying firms can cover all their costs and. Determining Price and Output under Monopoly. Price and Output Decisions under different Market Perfect Competition Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly.
In a competitive market competition among firms will drive down the price to the point where firms are not earning profits. Perfectly Competitive Output Markets. A monopolistic market and a perfectly competitive market are two market structures that have several key distinctions in terms of.
Start up costs and technology lots of training and know-how describe prices and output in a perfectly planned competitive market. Less of a good and charges a higher price. In addition at this point the quantity demanded and supplied is called equilibrium quantity.
If the price function P 20 Q and MC 5 2Q calculate the profit-maximizing price and output. At this point firms cannot lower prices further or they will lose money. If we treat the marginal cost of the monopolist as the counterpart of the aggregate marginal cost of the competitive industry its intersection with the market demand curve gives us the competitive market price and sales.
In perfectly competitive markets there is no differentiation of products making the firms that reside in these market price takers. A perfectly competitive market is characterized by many buyers and sellers undifferentiated products no transaction costs no barriers to entry and exit and perfect information about the price of a good. MC MR MC curve must cut MR curve from below.
Monopolistic Competitive Market Pricing Strategy. In perfect competition the price of a product is determined at a point at which the demand and supply curve intersect each other. This point is known as equilibrium point as well as the price is known as equilibrium price.
Price-Output Determination Given the conditions of perfect competition the market price is determined by the market forces Market demand and Market Supply The firm in a perfectly competitive market is a Price-taker not a Price-Maker Price Determination Rule. Less of a good and charges a lower price. More of a good and charges a higher price.
If the market price received by a perfectly competitive firm leads it to produce at a quantity where the price is greater than average cost the firm will earn profits. Therefore the farmer can sell as much wheat as he wishes at the market price but cannot sell any at a higher price because there is no demand for it. Short run is defined as a period of time when at least one input is fixed.
The initial equilibrium price and output are determined in the market for oats by the intersection of demand and supply at point A in Panel a. If the price received by the firm causes it to produce at a quantity where price equals average cost which occurs at the minimum point of the AC curve then the firm earns zero profits. Economics questions and answers.
By signing up youll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your. Each firm chooses an output level that maximizes profits. More of a good and charges a lower price.
If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. The perfect competitor face a completely horizontal demand curve 3. In a perfectly competitive market where the product is homogeneous and the price is determined by the market forces the quantity of output to be produced alters the profit.
The market is perfectly competitive with constant input prices and each firm has the same cost structure described by the following table. An increase in the market demand for oats from D 1 to D 2 in Panel a shifts the equilibrium solution to point B.
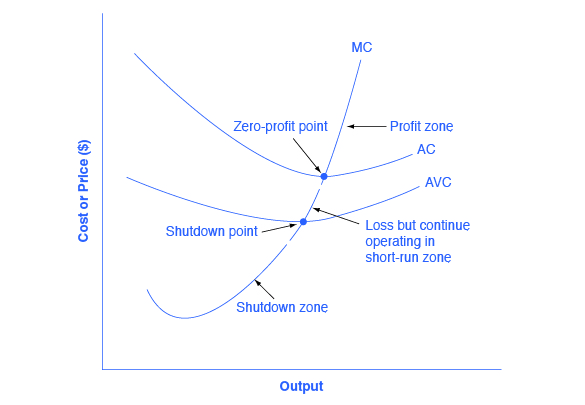
8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions Principles Of Economics

Price Determination Under Perfect Competition Equilibrium Of Firm
0 Comments